Orange Fiber
Case Study of a Sustainability Oriented Innovation
Co-written with Alice Cangemi, Maya Zakharia, and Ivanka Gutiérrez ⚡️
TLDR
Orange Fiber: Sicilian start-up founded in 2014
Innovative model: Extracts cellulose from citrus pulp, creates high-quality yarn for luxury fabrics
Business Model: Circular economy approach, partnering with companies like Lenzing Group
Impact: Influences consumer behavior and industry practices for a more sustainable future
Orange Fiber is an innovative Italian start-up that stands at the intersection of two pillars of Italian heritage — textiles and food. Founded in 2014 by Adriana Santanocito and Enrica Arena, the start-up is headquartered in Catania, Sicily, and has acquired international recognition for its unique approach to textile production.
In Italy, an annual production of over 700,000 tons of citrus waste underscores a significant environmental challenge. This start-up has uniquely positioned itself to address this issue by specializing in the creation of sustainable fabrics derived from citrus waste, with a particular focus on the abundant leftovers generated by the citrus juice industry in the country. This approach addresses two significant issues: the environmental impact of textile production and the disposal of citrus by-products. The start-up's innovation lies in transforming citrus waste, which would otherwise be discarded, into a valuable resource, thereby promoting a circular economy model.
By linking Orange Fiber's technological innovation to the cultural heritage of the orange industry in Sicily, the company was able to simultaneously create economic, environmental, and social value.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are guidelines for increasing the well-being of society and protecting the planet. Orange Fiber is working on making its processes as aligned with the SDGs as possible, especially with 5 out of the 17 SDGs.
SDG #9 “Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation”: To facilitate and have a more sustainable control on the planning and execution of transportation and storage, Orange Fiber only uses one plant for their production and the citrus pressing process.
SDG #12 “Ensure Sustainable Consumption and Production”: Since ethical and sustainable fabric production is based on upcycling orange fiber, they have reduced more than 80 tons of what otherwise would have been waste from juice production. In addition, to ensure a safe process that will comply with regulations they have a partnership with Lenzing Group.
SDG #13 “Take Urgent Action to Combat Climate Change and its Impacts”: According to Orange Fiber’s web page, their cellulose production causes approximately “40% less climate change impact” [measured in kg CO2 eq] compared to other similar processes.
SDG #15 “Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainable management of forests, combat desertification, reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss”: Avoiding the traditional wood dissolving pulp, the company reduces land degradation and avoids deforestation by avoiding traditional fabrics through the upcycling process, and the TENCEL™ Limited Edition x Orange Fiber thanks to the with partnership Lenzing.
SDG #17: “Strengthening the means of implementation and revitalize the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development”: With the help of social media and partnerships, the company spreads the message of conscious consumption, as well as the importance of innovative approaches in the textile and fashion industries.
Sustainability Oriented Innovation Driver
Orange Fiber's development is driven by various factors, with technological innovation standing out prominently. Orange Fiber is a pioneer in the patented technology for cellulose extraction from citrus fruit pulp. Transforming ecological chemicals into biodegradable fabric. Over the years, cellulose extraction has been used in the textile industry for materials such as viscose, however, with research and technological advancements, a more sustainable method has been developed. Collaboration with research institutes is vital for any technological development and Orange Fiber was no different. The start-up partnered with a laboratory at Milan Polytechnic to prove the viability of the process, marking their entry into the realm of sustainable textile and fashion.
Another driver contributing to the development of this Sustainable Oriented Innovation is the market pull. According to a survey conducted by McKinsey in 2020, 67% of those surveyed considered the use of sustainable materials as a significant factor influencing their purchasing decisions. The fashion industry has a large environmental impact ranging from contribution to greenhouse gases to high water consumption and waste disposal issues. Customers prefer sustainable products and clothes will always be in demand, this market pull is leading to several sustainable innovations in the fashion industry to be able to meet customer expectations and reduce the impacts on the environment. The increased need to be more transparent in the supply chain will also lead businesses to collaborate with start-ups who have a sustainable and transparent process. In 2023, Candiani, in collaboration with Orange Fiber and Progetto Quid, incorporated into the denim market the sustainable technological innovation of the former and the social value of latter. Fashion is moving in a sustainable direction and the start-up was able to utilize this market pull to grow.
The substantial generation of citrus waste in Italy poses notable economic and environmental challenges. Recognizing this, the founders of Orange Fiber seized the opportunity in the market to address this issue by aiming to minimize waste while simultaneously delivering value to their customers. By creating high-quality biodegradable textiles from waste, the Start-up was able to change the meaning of waste and redefine the issue by creating an upcycling solution to this problem in both the agriculture industry and the textile industry. Orange Fiber has collaborated with fashion brands and other textile producers, to position itself in the market and make their products more appealing to consumers.
The regulatory frameworks for sustainability have been evolving for a few decades now, especially in the EU. The Textile Regulation (EU) No 1007/2011 introduced measures to disclose fiber composition, identify sustainable fibers, and increase traceability in the supply chain, among other measures. With the push towards traceability and transparency, the signs that the industry was moving in the right direction related to sustainable fabric were present as of 2011 and the founders of Orange Fiber came up with the idea for the business in 2012. The trajectory of sustainable regulations paved the way for innovative solutions to grow and gain traction and current regulations such as the new circular economy action plan (CEAP) by the EU will further push the fashion industry to start using sustainable fibers and to continue to innovate for a better future.
Value Drivers
Orange Fiber focuses on leveraging impact through the triple-bottom line: economic, sustainable, and social factors. This approach is aimed at providing value for their customers, stakeholders, and shareholders in the following way:
Economic Value: Reducing food waste can lead to significant cost savings for businesses and the economy as a whole. Transforming waste into high-quality fabrics, Orange Fiber contributes to resource efficiency and cost reduction in waste management. Also, their unique market positioning of the fabric is suited for luxury and premium brands. This focus on high quality allows the start-up to command premium prices that can potentially enhance high economic returns therefore supporting the regional economy.
Sustainable Value: Citrus juice production leads to the generation of waste which is practically 60% of the fresh fruit mass. Repurposing citrus pulp waste into valuable textiles directly addresses environmental sustainability. Their process reduces the environmental impact of waste disposal and promotes circular economy. Also, the use of local citrus waste from Italy contributes to a smaller carbon footprint and reinforces the concept of local sourcing.
Social Value: Orange Fiber's commitment to innovative patented formulas and production processes contributes to the textile industry advancement. The company's participation in an international network of innovators, including the partnership with Lenzing Group, indicates a commitment to knowledge sharing and collaboration, which provides benefits for the community overall.
Typology Identification
Orange Fiber aims to create organizational transformation to unlock new market opportunities. Their primary goal is to develop innovative products that have a positive impact. As a result, their efforts align with shared value principles and bring about a fundamental shift in the industry. To achieve this, Orange Fiber has integrated sustainability and innovation into their culture and operations through long-term collaborations:
Special projects: Innovation through the eyes of Orange Fiber goes beyond creating fabrics for the runway. They have demonstrated out-of-the-box thinking and curiosity by collaborating on transformative projects like TECLA 3D House. Partnering with the first eco-sustainable house 3D printed from local raw earth, is one example that showcases Orange Fiber’s flexibility. They designed all the fabrics used with the furniture elements of this innovative project.
Exhibitions: Orange Fiber is part of Grow, the new exhibition of the Fashion For Good Museum in Amsterdam dedicated to biomaterials and innovations that are shaping the future of fashion. In 2020, they were also selected to be part of “Future Food. How will we eat tomorrow?”, an innovative exhibition dedicated to food installed at the Deutsches Hygiene-Museum in Dresden.
Collaborating with other Brands: Orange Fiber has been successful in combining brand essences to create unique luxurious pieces. Partnering with brands like Ferragamo and E. Marinella shows that Orange Fiber has the fabric quality necessary to be represented as a luxurious innovation. They have also collaborated with brands like H&M, which demonstrates that Orange Fiber values accessibility and achievability of their products.
The Sustainable Business Model
Orange Fiber’s sustainable business model transforms waste into value by adopting a Circular Economy manufacturing approach in contrast to a linear economy process. The innovative alternative to conventional textile materials initiates with the extraction of cellulose from orange juice leftovers obtained from companies involved in orange juice production. To streamline the supply chain, Orange Fiber strategically places its plant inside the partnering company’s plant. Subsequently, following their proprietary processes, the extracted cellulose undergoes optimization and purification to transition into fiber, marking a significant step in their patented production method.
According to the Council of Fashion Designers of America their lyocell fibre has the OEKO-TEX Standard 100 product class I, which means it is not toxic for the environment. In addition to this, their materials are classified by the CFDA as biodegradable, cellulose, wood, or plant-based, natural waste, and vegan. Enrica Arena CEO and Co-founder of Orange Fiber, explains in an interview that “in the case of lyocell and ion liquid spinning the most interesting aspect is that most of the solvent is recycled during the process, minimizing the environmental impacts”.
This model enters the category of industrial symbiosis, since the citrus juice industry and the textile industry collaborate to promote the re-valorisation of waste, resource efficiency and reduction of environmental impact. The symbiosis avoids the costs from getting rid of the citrus waste and instead increases revenue for the user company.
Orange Cycle is being assessed by two bodies that will examine their supply chain and the extraction of cellulose for them to continue to improve their processes. They have been investing resources and R&D time for approximately 8 years, and continuous support from public and private sector are still needed to continue the path towards sustainable and circular business models in the textile industry.
Circular Economy Process
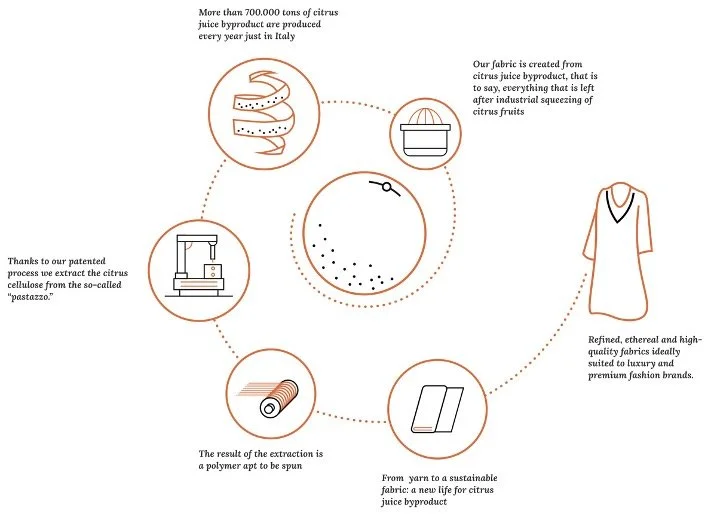
The process of creating Orange Fiber's fabric begins with the collection of “hundreds of thousands” of tons of citrus juice by-products, primarily from Sicilian citrus juice producers. This waste, colloquially known as “pastazzo”, accounts for 60% of the weight of the fresh fruit (mainly of peels) rich in cellulose, which is the key ingredient for fiber production. The cellulose is extracted through a patented process - first laboratory experimented with the support of Politecnico of Milano - which minimizes the use of chemicals and water compared to traditional textile production methods.
This technology extracts cellulose from this citrus pulp to create a polymer, which undergoes a spinning process and is then transformed into a high-quality yarn. This yarn can then be blended with other materials or used in its pure form. The resulting fabric is characterized by its lightweight, silky texture, and high quality, comparable to other luxury fabrics like silk, that can be opaque or shiny according to production needs.
This process derives from an open system that began with the collaboration with Politecnico di Milano and continues to be part of the company. Through continuous innovation partnership with Lenzing Group, the fiber processed with them is made of orange and wood pulp (from certified forests) and is called TENCEL™ branded Lyocell fiber. Hence, Lenzing is a key factor in the upcycling process and the closed-loop system in the supply chain. In this way, there is an open business model due to the collaboration for value creation. Lenzing is based in Austria, where is processed and then is shipped back to Italy to be transformed into yarn. Since the dyes used are also completely natural, the biodegradable fabric could be used to make compost.
Consequently, the useful application of materials that are already available (by-product of orange juice) allows fewer natural raw resources to be needed and therefore there is less environmental pressure, such as reducing land degradation and deforestation.
The start-up has also initiated a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of the impact of its activities to ensure both economic and environmental sustainability of the operations, to figure out how to optimize them. This process involves a close examination of water usage, carbon footprint, overall efficiency, and the impact of by-products. The goal is to ensure that resources are used to their fullest potential, enhancing value at every stage. Given the highly innovative nature of both their products and processes, ongoing research and development are crucial for continuous improvement and refinement of their operational model.
Conclusion
Orange Fiber's role in the circular economy process is exemplified by their unique fabric creation. Through upcycling citrus waste and collaboration Orange Fiber creates value across economic, environmental, and social domains. As they continue to lead the way in sustainable textile innovation, the impact of their efforts extends beyond the fashion industry, influencing consumer behavior, industry practices, and contributing to a more sustainable and circular future. Orange Fiber is a complete case study of a sustainability-oriented innovation that has the potential to transform the way the industry behaves today.
Sources:
Orange Fiber: https://orangefiber.it/heritage/
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): https://sdgs.un.org/goals
Orange Fiber Impact Report: https://orangefiber.it/impact/
Mckinsey Survey: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/survey-consumer-sentiment-on-sustainability-in-fashion
The Sportswear Magazine: https://www.thesportswear.it/candiani-denim-coreva-design-capsule-collection/
EU. The Textile Regulation (EU) No 1007/2011: www.eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32011R1007
Circular Economy Action Plan: www.environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/circular-economy-action-plan_en
Citrus fruit processing waste - A scientific outlook: www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772502222000105#bib0125
Mario Cucinella Architects- TECLA 3D House: www.mcarchitects.it/en/projects/tecla-technology-and-clay
Grow Exhibit, Fashion for Good Museum: https://fashionforgood.com/our_news/fashion-for-goods-new-exhibit-grow-shows-the-future-of-fashions-materials/
Future Food, what will we eat tomorrow? Exhibit, Deutsches Hygiene-Museum: https://www.dhmd.de/en/exhibitions/archive/future-food
Ferragamo X Orange Fiber: https://group.ferragamo.com/it/news/2017/orange+fiber
E. Marinella X Orange Fiber: https://www.emarinella.eu/category/orange-fiber-en/
H&M X Orange Fiber: https://hmgroup.com/our-stories/orange-fiber/
Orange Fiber: a sustainable brand that produces luxury textiles using citrus juice by-products: https://associatedmedias.com/en/orange-fiber-a-sustainable-brand-that-produces-luxury-textiles-using-citrus-juice-by-products/
Optimising Environmental Performance of Symbiotic Networks Using Semantics: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63456-6.50142-3.
Interview with Orange Fiber: circular economy and industrial symbiosis for more sustainable fashion: www.cikis.studio/en/article/interview-with-orange-fiber-circular-economy-and-industrial-symbiosis-for-more-sustainable-fashion
Industrial Symbiosis In The Production Of Sustainable Textiles: Orange Fiber: https://www.procedia-esem.eu/pdf/issues/2022/no4/19_120_Torrisi_22.pdf